top of page
เลือกภาษา

Search


Cholesterol, Statins, and the Question We Keep Avoiding
A large new meta-analysis published in The Lancet has reignited the statin debate. Headlines quickly followed: “ Most statin side effects are overblown ” and “ Millions more people should be taking statins.” The study itself is substantial. By pooling data from nearly 20 large, double-blind randomized trials with over 120,000 participants, the authors examined whether statins truly cause the long list of side effects commonly blamed on them. Their conclusion was clear: f
Feb 114 min read


When Inflammation Isn’t an Attack — It’s Gridlock
What a new Science study reveals about obesity, mitochondria, and why inflammation won’t turn off Low-grade inflammation is one of the most consistent features of obesity. It shows up in blood tests, adipose tissue, the liver, the brain — and it strongly predicts diabetes, cardiovascular disease, fatty liver disease, and even neurodegeneration. But one question has lingered for years: Why does inflammation persist even when there’s no infection to fight? A new study publish
Feb 104 min read


When Raising NAD⁺ Isn’t Enough: Energy Flow vs Energy Supply
What a new human study reveals about NAD⁺ boosters, mitochondria, and why energy flow matters more than supply For the past decade, NAD⁺ has become one of the most talked-about molecules in aging, brain health, and metabolic medicine. Low NAD⁺ has been linked to fatigue, neurodegeneration, inflammation, and accelerated aging. Naturally, the idea followed: restore NAD⁺, restore health. This logic underlies influential NAD-centric frameworks , including those popularized by Chr
Feb 94 min read


Diversity Is Not a Trend — It’s a Record of Survival
When we talk about “ diversity ” in health, we often mean it loosely: more variety is better, less is worse. In nutrition, in the microbiome, even in lifestyle advice, diversity has become shorthand for resilience. But biologically, diversity is not a lifestyle choice. It’s a record. A recent review in Trends in Molecular Medicine takes this idea seriously by focusing on the adaptive immune receptor repertoire (AIRR) — the vast collection of T-cell and B-cell receptors tha
Feb 84 min read


Aging Is Not Random Wear-and-Tear — It Is Bioenergetic Triage
For decades, aging has been described as a slow accumulation of damage: oxidative stress, genomic instability, misfolded proteins, random cellular failure. But what if aging is not primarily about damage at all? What if it is about what the body can no longer afford to maintain? A newly published study in GeroScience adds powerful evidence to this alternative view — and strongly supports the idea that bioenergetic capacity sits at the center of aging, structural loss, and fu
Feb 63 min read


Cholesterol, Longevity, and a Missing Middle
Re-thinking Lipoproteins Through an Adaptation Lens A recent review on lipoprotein metabolism and life expectancy proposes an appealing idea: that lipoproteins are not just passive cholesterol carriers, but active participants in aging biology, interacting with major longevity pathways such as AMPK, mTOR, and sirtuins . At first glance, the framework seems elegant. Different lipoprotein classes are visually linked to nutrient-sensing pathways, and those pathways are in turn
Feb 53 min read


Melatonin, Rhythm, and Mitochondrial Traffic
Why sleep, fasting, and timing matter more than pushing output A recent comprehensive review on melatonin as a mitochondrial regulator adds an important layer to how we understand health, aging, and recovery. While the paper focuses on neurodegenerative disease, its real contribution goes beyond neurology. When read through the lens of ERM mitochondrial mechanics , it helps clarify why rhythm, sleep, fasting, and hormetic cycling work —and why they so often fail in modern li
Feb 44 min read


You Don’t Need Fancy Tests to See Early Breakdown — You Need the Right Lens
Modern medicine often assumes that earlier detection and better personalization require ever more sophisticated tests—omics panels, advanced imaging, novel biomarkers. A recent study published in BMC Medicine (2026) quietly challenges that idea and, in doing so, strongly supports a core principle of the Exposure-Related Malnutrition (ERM) / stress-adaptation framework : The signal is already in routine clinical data—if we read it as patterns, not cut-offs. What the study a
Feb 33 min read


When Mitochondria Keep Signaling but the Body Can’t Recover
What Picard (2022) and a new Molecular Cell review get right—and what they still miss For a long time, mitochondria were taught as simple “power plants”: make ATP, keep the lights on, move along. That story is now clearly outdated. Over the past few years, a new view has emerged—one that sees mitochondria as communication hubs that sense stress, coordinate responses, and signal to the rest of the cell and body. Two influential works sit at the center of this shift: Martin P
Feb 23 min read


Epigenetic Drift Isn’t Random — It’s What Happens When Cellular Energy Gets Stuck
For a long time, aging has been described as epigenetic drift —a gradual loss of chromatin organization, where genes that were once tightly regulated become noisy, disordered, and harder to control. But “drift” makes it sound accidental. As if the genome simply forgets itself over time. What if that’s not what’s happening at all? Recent research suggests a more grounded explanation: epigenetic drift may be the visible footprint of metabolic congestion—when cells no longer hav
Feb 14 min read


Activation ≠ Clearance
What a Chemical Reprogramming Study Reveals About Mitochondrial Congestion A recent Aging Cell study set out to test an exciting idea in longevity science: Can we rejuvenate tissues in living mammals using a chemical “partial reprogramming” cocktail—without genetic manipulation? What the authors found is more important than rejuvenation itself. The intervention strongly activated mitochondria, epigenetics, and metabolic signaling —yet ATP fell, redox balance worsened, and l
Jan 313 min read


Aging Isn’t Just Damage — It’s Congestion
What extracellular vesicles reveal about recovery, mitochondria, and aging For a long time, aging has been explained as a slow accumulation of damage: broken DNA, worn-out mitochondria, inflamed tissues, and cells that eventually stop functioning. This idea is intuitive—but it leaves an important question unanswered: Why do many aging cells remain alive, metabolically active, and highly responsive to stress signals, yet unable to recover? A recent study published in Aging Ce
Jan 304 min read


When Stress Becomes Exhaustion: What the Brain’s Salience Network Reveals About Resilience
Why do some people bend under stress and recover—while others become increasingly sensitive, overwhelmed, and depleted? A growing body of neuroscience suggests the answer is not how much stress the brain detects , but whether it still has the energy to act on that information . A recent single-cell study published in Cell Reports (2026) offers an important clue. Instead of focusing on what “goes wrong” in stress-related conditions, the researchers asked a different question:
Jan 293 min read


Your Body Makes Cholesterol for a Reason
Why LDL Rises Under Stress—and What We Should Do About It For decades, cholesterol has been framed as the villain of cardiovascular disease. High LDL? Suppress it. Lower is better. End of story. But biology is rarely that simple. A recent review in Clinical Research in Cardiology (2026) , “A practical guide to the management of dyslipidaemia,” offers an important—if still incomplete—update to how modern medicine thinks about cholesterol. When read carefully, it reveals a de
Jan 283 min read


NAD⁺, Anti-Aging Hype, and the Mitochondrial Traffic Jam
Why NAD⁺ “works” in some studies—and fails in many real people Every few years, a molecule becomes the new darling of longevity science. For the past decade, that molecule has been NAD⁺ . Boost your NAD⁺, we’re told, and you can: Rejuvenate mitochondria Restore energy Slow aging Improve brain and muscle function A new study published in JCI Insight adds more fuel to this narrative, showing that NAD⁺ precursors can dramatically improve mitochondrial function and behavior in a
Jan 273 min read


Measuring Aging Is Not the Same as Preventing It
Why resilience needs a framework of stress adaptation—not just biological clocks A recent editorial in C linical and Translational Medicine by Hernandez and Ibanez makes an important and timely proposal: aging research should move beyond vulnerability and disease risk, and begin to study resilience —why some individuals age well despite adversity. To do this, the authors introduce the idea of expotype–phenotype resilience and propose using multimodal aging clocks (epigene
Jan 263 min read

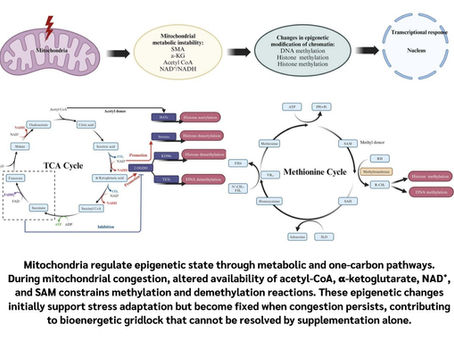
Why Methylation Problems Are So Common—and Why Supplements Often Aren’t Enough
What Mitochondrial Congestion Teaches Us About Stress, Aging, and Methylation We often talk about aging and chronic disease as if they are caused by damage —wear and tear slowly accumulating over time. But a growing body of science is pointing in a different direction: many age-related problems arise not because the body fails to respond to stress, but because it responds for too long, without being able to fully recover . A recent review by Inter- and intracellular mitochon
Jan 243 min read


Aging Is Now Measurable — But Recovery Is the Bottleneck
As Nature Aging marked its fifth anniversary, the journal asked many of the field’s most influential scientists a deceptively simple question: what have we learned about aging, where are we headed, and what still stands in the way? Taken together, the answers form something rare in modern biomedicine: a broad, cross-disciplinary convergence . Not on a miracle therapy or a single pathway—but on a shared reframing of what aging is , what medicine can realistically do about it,
Jan 234 min read


Aging, Regeneration, and the Missing Rhythm: When Models Jump Too Quickly to Intervention
In recent years, aging science has moved decisively away from the idea of aging as a fixed, irreversible decline. Instead, many contemporary models frame aging as a dynamic, potentially modifiable process shaped by stress, repair, and recovery capacity. Among these, a recent review proposing a “ regeneration model of aging ” adds another thoughtful voice to the conversation. The core proposal is appealing: aging reflects a failure of regeneration rather than the inevitable
Jan 223 min read


Beyond Hormones: Completing the Geroprotection Puzzle in Women’s Aging
For decades, hormone replacement therapy (HRT) has been framed narrowly—as a way to relieve hot flashes, improve sleep, or manage menopausal symptoms. A recent Perspective published in Aging and Disease challenges this limited view, arguing that perimenopausal HRT should be reconsidered as a potential geroprotective intervention , capable of influencing long-term healthspan rather than just short-term comfort. This is an important and timely reframing. But to fully realize
Jan 213 min read
bottom of page