top of page
เลือกภาษา

Search


Why Aging Is Not a Signaling Problem: Insights from Geroscience and Mitochondrial Recovery
In a recent geroscience review, Nicoletti et al. (2025) synthesize decades of research on the core nutrient- and stress-sensing pathways that dominate modern aging biology— mTOR, AMPK, sirtuins, IGF-1/GH, and NAD⁺ metabolism . Their message is both familiar and important: aging is shaped by conserved biological programs that continuously sense energy availability, stress, and growth signals, and then recalibrate physiology accordingly. But when this review is viewed through
Jan 193 min read


Triglycerides: From “Secondary” to Center Stage in Cardiovascular Prevention
For decades, cardiovascular prevention has revolved around one dominant target: LDL cholesterol . Triglycerides were often treated as a side note—something to “clean up” after LDL-C goals were met, or a marker of poor lifestyle rather than a causal driver of disease. That framing is now changing. A recent state-of-the-art review by Toth and Banach, on behalf of the International Lipid Expert Panel , positions 2025 as a turning point : the year triglycerides moved from a secon
Jan 173 min read


Regulation vs. Execution: The Bioenergetic Bottleneck in Aging
For a long time, aging and chronic disease have been explained as the gradual accumulation of damage—oxidative stress, inflammation, cellular wear and tear. But an emerging body of science is pointing to a different conclusion: The problem is not that the body doesn’t know how to recover.The problem is that it often can’t afford to. A recent review proposes that aging is driven by dysregulation of the autonomic nervous system —specifically, an imbalance between the sympatheti
Jan 153 min read


NAD⁺ Depletion and the Biology of Exhaustion
We’ve long known that chronic stress is harmful . We’ve also known that mitochondria and NAD⁺ sit at the heart of aging and chronic disease. What has remained unclear is why people can appear metabolically “stable” for years—sometimes decades—while slowly losing resilience, recovery capacity, and health. A recent study by Chaubey et al. (2026) offers a crucial piece of that puzzle. Their findings align remarkably well with the Exposure-Related Malnutrition (ERM) framework
Jan 143 min read


When Cells Run Low on Energy, They Don’t Just Slow Down — They Make a Decision
What a new study reveals about senescence, mitochondria, and recovery failure Recent work published in iScience by Akakura and Tabibzadeh (2026) delivers a striking message: cellular senescence is not simply the end result of accumulated damage—it is an active, regulated decision that emerges when bioenergetic buffering collapses . Even more importantly, the study shows that this decision can be reversible , provided key metabolic–epigenetic supports remain intact. This find
Jan 133 min read

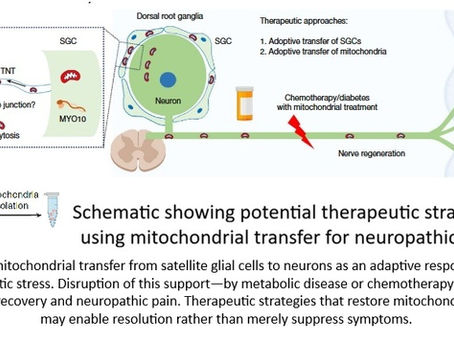
Why Stress Doesn’t Break Us—But Failed Recovery Does
New evidence places mitochondria at the center of aging, pain, and metabolic dysfunction For decades, stress has been blamed as the primary driver of aging, chronic disease, and burnout. Too much cortisol. Too much inflammation. Too much pressure on the nervous system. But a growing body of research is telling a different story. Stress, it turns out, is not the real villain. Failed recovery is. A newly published study in Nature adds powerful biological evidence to this shift
Jan 103 min read


Our New Publication: Human Evidence That Chronic Stress Ages Us Through Bioenergetic Debt
We’re pleased to share that our review has just been published in Biogerontology . In this paper, we synthesize human evidence showing that chronic psychological stress accelerates biological aging not primarily through irreversible DNA damage—but through progressive failure of energetic recovery , a process we describe as bioenergetic debt . This work brings together longitudinal human data, mitochondrial biology, and telomere science, and provides direct empirical suppor
Jan 73 min read


Deep Rest: Why Recovery Is an Active Biological Process — and Why Many People Never Reach It
For years, we’ve been told that rest is the antidote to stress . Sleep more. Slow down. Take a break. But what if rest alone isn’t enough? A recent scientific review published in Health Psychology Review introduces a powerful idea that helps explain why so many people feel exhausted, inflamed, or unwell even after stressors are removed . The authors call this state “deep rest.” And importantly, they show that deep rest is not the same as stopping activity or lying down . It
Jan 63 min read


Another Review Confirms the Problem — But Integration Is Still Missing
Why mitochondrial dysfunction links aging, insulin resistance, and inflammation — and why medicine still treats them separately. A recent review published in Metabolites (2025) by Hao et al., “Relationship of Ageing to Insulin Resistance and Atherosclerosis” , delivers a clear and important message: Aging, insulin resistance, chronic inflammation, and atherosclerosis are not separate diseases — they are biologically connected through mitochondrial dysfunction. This is not a
Jan 53 min read


Buffering Aging vs Reversing It: A Tale of Two Longevity Strategies
What a new longevity study gets right, what it doesn’t, and why mitochondria still sit at the center A recent mouse study has generated excitement by showing that very old, frail animals can live longer and function better when two age-shifted signals are corrected together: oxytocin (OT) and TGF-β signaling (via ALK5 inhibition) . At first glance, the results look like “rejuvenation .” But when viewed through a bioenergetic lens, the study tells a more nuanced—and more im
Dec 31, 20253 min read


When Aging Becomes a Reversible Energy State
What two new studies tell us about mitochondrial reversibility and hope for metabolic recovery For decades, aging has been framed as a one-way street : damage accumulates, mitochondria fail, and decline is inevitable. But a growing body of research is quietly changing that story. Two recent studies —one dissecting how cells get stuck i n an aging metabolic state, and another showing how that state can be nudged back toward recovery —together support a more hopeful, systems-b
Dec 30, 20253 min read


Aging Isn’t Just Wear and Tear — It’s an Energy Problem
What young blood vesicles teach us about mitochondria, ERM, and the future of geromedicine For decades, aging has been framed as an unavoidable accumulation of damage: broken DNA, worn-out proteins, failing cells. But a growing body of research is challenging that story. A recent study titled “Small extracellular vesicles from young plasma reverse age-related functional declines by improving mitochondrial energy metabolism” adds a powerful new piece of evidence — suggesting
Dec 29, 20253 min read


Beyond Blood Sugar: Why Insulin Matters Long Before Diabetes
For decades, metabolic health has been judged largely by blood sugar . If glucose is “normal,” we reassure. If it rises, we intervene. But a growing body of evidence suggests this approach is too late . A recent perspective in Diabetes Care titled “Beyond Glucose—Rethinking Prediabetes for Precision Prevention” makes this problem explicit. The authors argue that what we call prediabetes is not a single condition, but a collection of distinct metabolic states , each with di
Dec 27, 20253 min read


When Fuel Is Abundant, but Energy Is Scarce
Lactate, LDH, and Futile Lipid Cycling in the ERM Framework For decades, lactate has been misunderstood. Often labeled as a waste product or a marker of “ anaerobic metabolism ,” it has been blamed for fatigue, poor performance, and disease. A major symposium review in The Journal of Physiology helps finally put this misconception to rest—and in doing so, it provides strong mechanistic support for a central idea in the Exposure-Related Malnutrition (ERM) framework: glycolyt
Dec 26, 20253 min read


When the Body Can’t Afford to Waste Energy
Futile Lipid Cycling, ERM, and the Hidden Logic of Metabolic Breakdown For years, metabolism was taught with a simple rule: efficiency is good, waste is bad . But modern physiology tells a more nuanced story. Some forms of “ waste” are not mistakes at all—they are protective design features . One striking example is futile lipid cycling , a process long misunderstood and now recognized as a cornerstone of metabolic resilience. A recent Nature Metabolism review reframes futi
Dec 25, 20253 min read


From Stress Response to Recovery
What New Mitochondrial Science Confirms—and What ERM Adds Two recent papers, published independently in leading journals, arrive at a strikingly similar conclusion: stress is not damaging because it activates biology—but because it consumes energy, and recovery fails when that energy debt cannot be repaid . Together, they help explain how stress becomes disease. The Exposure-Related Malnutrition (ERM) framework helps explain why this matters clinically—and what to do next
Dec 23, 20253 min read


When Too Much Fuel Breaks the Engine
Glycolytic Overload, Fatty Liver, and the Hidden Energy Crisis For years, metabolic diseases like fatty liver have been framed as a simple problem of too many calories . Eat less sugar, burn more fat, and the problem should resolve. But a new 2025 review in Clinical Science challenges this oversimplified view—and in doing so, quietly supports a deeper concept: disease emerges not just from excess intake, but from failure of metabolic resolution . A new thesis: glycolytic ove
Dec 22, 20253 min read


Why the “Methylation Cycle” Is Not Just About Folate or Vitamin B12
When people hear methylation , they often think about folate or vitamin B12 supplements . While these nutrients are important, this framing misses the much bigger—and far more powerful—biological story. At its core, the methionine cycle is the cell’s methyl-production and regulation system . It governs how genes are turned on or off, how proteins function, and how cells decide between growth, repair, and defense. Even more importantly, this cycle is directly connected to re
Dec 21, 20253 min read


When Healing Stalls: Why Energy, Not Inflammation Alone, Determines Recovery
We often think of healing as something the body does automatically . Cut the skin, fight the infection, calm the inflammation—and recovery should follow. But what if healing doesn’t fail because the signal is wrong…What if it fails because the energy to complete the job is no longer available ? A recent study published in Cell Metabolism offers a striking demonstration of this idea—and helps explain a central concept behind Exposure-Related Malnutrition (ERM) . Healing Is a
Dec 19, 20253 min read


What We Still Don’t Know About Aging
Why Energy, Recovery, and Resilience Matter A new paper in GeroScience by Talay and colleagues (2025), titled “Open problems in ageing science: a roadmap for biogerontology,” does something both rare and valuable in modern science: it pauses progress long enough to ask what we still don’t understand . Rather than proposing another intervention or biomarker, the authors curated 100 open questions that remain unresolved in aging research—from the molecular to the clinical le
Dec 18, 20254 min read
bottom of page